Introduction
In today’s online world, staying safe is very important. Cybercriminals are always trying to steal data or harm systems. This is a big problem for people, companies, and even governments. The old ways to stop these attacks don’t work well anymore.
This is where Machine Learning (ML) helps. It is smart technology that can find and stop threats quickly. It helps make online safety much better.
In this full guide from AI Vixor, you will learn how machine learning is changing cybersecurity. We will explain its methods, uses, advantages, problems, and what we can expect in the future — all in very simple English.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a part of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It teaches computers to learn from data and make smart choices on their own. It does not need someone to write every rule.
Machine learning systems study large amounts of data, find patterns, and improve over time. They get better as they see more data. This makes ML very useful for cybersecurity, where new threats appear all the time.
Key Components of Machine Learning
Algorithms
Algorithms are the steps or rules that a computer follows to understand data. They help the system find useful information and make decisions. Some common ML algorithms used in cybersecurity are:
- Decision Trees
- Neural Networks
- Support Vector Machines
Each one helps solve different types of security problems.
Data Sets
ML systems need a lot of data to learn. This includes both normal activity and harmful activity (like viruses or attacks). Good quality data helps the system become smart and accurate.
Training Models
This means teaching the ML system using the data. There are three common ways to train:
- Supervised Learning: The data is labeled, so the system knows what is right or wrong.
- Unsupervised Learning: The data is not labeled; the system finds patterns itself.
- Reinforcement Learning: The system learns by trying things and getting rewards or feedback.
Evaluation
Once the model is trained, we test it to check how well it works. We use real-world data to see if it can find threats correctly. If needed, we will improve the model to make it stronger.
The Role of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Machine learning is helping cybersecurity in many ways:
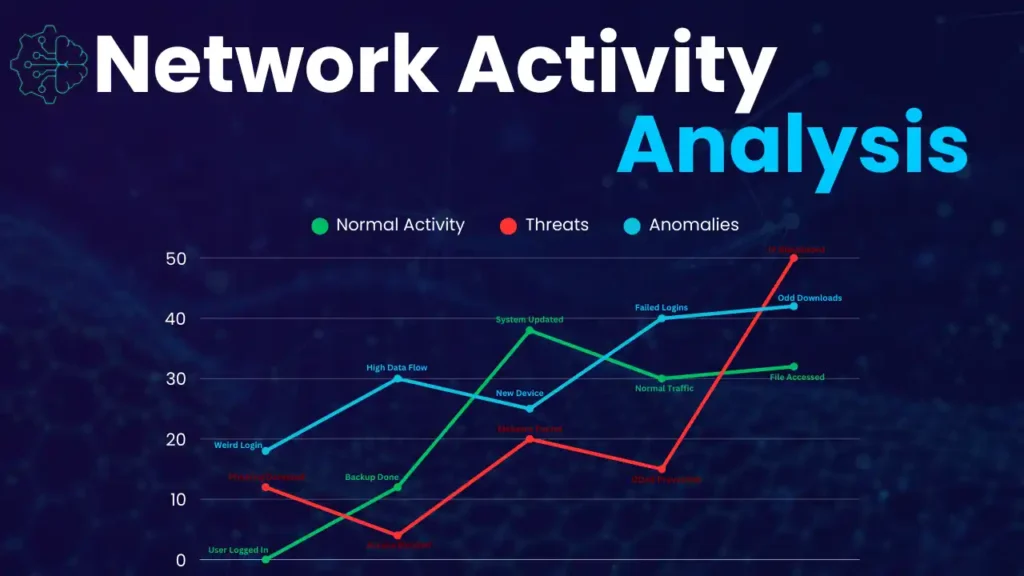
- Threat Detection:
Identifying malware, phishing attempts, and other threats in real-time by analyzing patterns in network traffic, user behavior, and file attributes. - Anomaly Detection:
Learning what normal system behavior looks like and flagging unusual activities, such as sudden changes, to alert security teams. - Predictive Analysis:
Analyzing past cyberattacks to predict potential future threats, helping security teams prepare and defend in advance. - Automated Responses:
Taking immediate action when a threat is detected, such as blocking malicious IPs or isolating infected systems, without waiting for human intervention.
Machine Learning Techniques Used in Cybersecurity
1. Supervised Learning
- Use Case: Spam detection, intrusion detection, and malware classification.
- How It Works: Models are trained on labeled datasets, learning to classify threats accurately. By analyzing past cyber incidents, supervised learning models can recognize similar threats in new data streams. For example, email security systems use supervised learning to filter out spam and phishing emails based on labeled examples.
2. Unsupervised Learning
- Use Case: Anomaly detection, identifying unknown threats, and clustering similar behaviors.
- How It Works: Analyzes data without pre-existing labels to find hidden patterns. Unsupervised learning is particularly useful for detecting zero-day exploits and unknown malware by identifying deviations from normal behavior in network traffic and user activities.
3. Reinforcement Learning
- Use Case: Adaptive security systems, automated response mechanisms, and dynamic threat hunting.
- How It Works: Systems learn by receiving feedback from their actions, improving over time. In cybersecurity, reinforcement learning can help in developing systems that adapt to new attack strategies by learning from simulated attack-defense scenarios.
Applications of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity

- Malware Detection: Using ML algorithms to identify malicious software by analyzing file behaviors, code patterns, and execution flows.
- Phishing Prevention: Recognizing fraudulent websites and emails by examining URLs, domain characteristics, email headers, and textual patterns.
- Network Security: Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities such as unusual data transfers, unauthorized access attempts, and abnormal communication patterns.
- Endpoint Protection: Securing devices connected to the network by identifying compromised devices and preventing the spread of threats across the network.
- Fraud Detection: Preventing financial and identity-based fraud by analyzing transaction patterns and user behavior.
Conclusion
Machine learning offers a powerful toolkit for modern cybersecurity strategies. By leveraging data-driven insights and automation, organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats and build more resilient security infrastructures. As cyber threats continue to grow in complexity, adopting machine learning in cybersecurity will not only be an advantage but a necessity for robust digital protection. Organizations that effectively integrate machine learning into their cybersecurity frameworks will be better equipped to safeguard their assets and maintain trust with their stakeholders.
✨ I hope you found this guide on Machine Learning in Cybersecurity helpful! If you enjoyed reading it or learned something new, do let me know. Your feedback keeps me motivated to bring more detailed and valuable content! 🚀😊










[…] in cybersecurity uses powerful machine learning (ML) algorithms to scan large data sets and spot unusual activities in real-time. Unlike […]